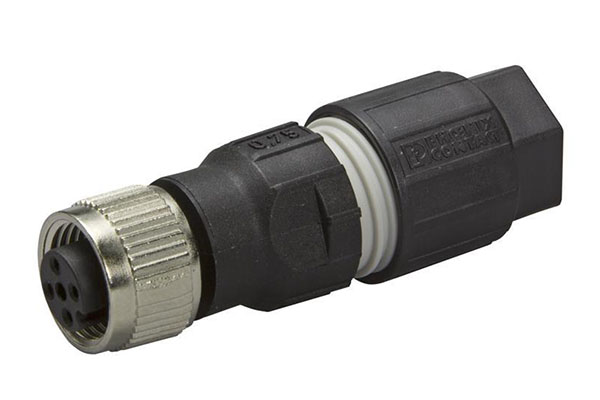
The world of cables can be complex, with various types and coding systems to consider. In the realm of industrial connectivity, M12 cables are widely used due to their robustness and reliability. However, one crucial aspect of M12 cables that often perplexes users is cable coding. In this blog post, we will decode M12 cable coding to help you understand its significance and choose the right coding type for your specific needs.
Understanding M12 Cable Coding
Before diving into the different types of M12 cable coding, let’s first grasp the concept of cable coding itself. Cable coding refers to the unique configuration of pins and keying on a connector, which ensures that the cable can only be connected to a compatible mating connector. It plays a vital role in preventing incorrect connections and ensures proper data transmission and power delivery.
M12 cables are available in several coding options, each designed for specific applications. Let’s explore the various types of M12 cable coding:
A-Coded M12 Cables
The A coded M12 cables are primarily used for sensor and actuator connections. They feature a single keyway and two to five pins, making them suitable for low-power applications. A-coded cables are often color-coded in black and have a 1/2-20 UNF thread.
Applications: Industrial automation, machine tools, sensor networks.
Pros: Simple and cost-effective, widely available.
Cons: Limited pin count and power capacity.
B-Coded M12 Cables
B-coded M12 cables are commonly used for Ethernet and fieldbus applications, including Industrial Ethernet and PROFINET. They have a unique keyway and four or five pins, enabling higher data transmission rates. B-coded cables are typically color-coded in white and have a 1/2-20 UNF thread.
Applications: Industrial Ethernet, PROFINET, fieldbus networks.
Pros: Suitable for high-speed data transmission, widely adopted in industrial automation.
Cons: Limited power capacity compared to other coding types.
D-Coded M12 Cables
D-coded M12 cables are specifically designed for Ethernet applications, offering higher data rates than A and B-coded cables. They feature a unique keyway and four or eight pins, providing a balance between data transmission and power capabilities. D-coded cables are often color-coded in green and have an M12 x 1.5 thread.
Applications: Ethernet, fieldbus, and PROFINET applications requiring higher bandwidth.
Pros: Higher data transmission rates, increased pin count.
Cons: Limited power capacity compared to some other coding types.
X-Coded M12 Cables
X-coded M12 cables are the latest addition to the M12 family and offer the highest data rates. They are specifically designed for high-speed Ethernet applications such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet. X-coded cables have a unique keyway and eight pins, ensuring reliable and fast data transmission. X-coded cables are typically color-coded in purple and have an M12 x 1.5 thread.
Applications: 10 Gigabit Ethernet, high-bandwidth industrial applications.
Pros: Highest data transmission rates, backward compatible with A, B, and D-coded connectors.
Cons: Limited power capacity compared to other coding types.
Choosing the Right M12 Cable Coding
Selecting the appropriate M12 cable coding requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, vibration, and exposure to chemicals. Certain coding types may offer better resistance and protection against these conditions.
Industry Standards and Requirements: Verify if your industry or specific application has any recommended or mandated coding standards. Compliance with these standards ensures compatibility and interoperability.
Connectivity Needs and Compatibility: Determine your specific connectivity requirements. Consider the type of equipment or devices you need to connect, their interface specifications, and compatibility with different coding types. Ensure that the chosen coding type matches the connectors on both ends of the cable for seamless integration.
The decision-making process involves weighing the pros and cons of each coding type based on your unique requirements. Consider practical examples and scenarios relevant to your application to gain a better understanding of which coding type aligns best with your needs.
For instance, if you are setting up an industrial automation system with sensor networks, A-coded M12 cables might be the most cost-effective and readily available option. On the other hand, if you require high-speed data transmission for an Industrial Ethernet network, B-coded or D-coded M12 cables could be more suitable.
FAQs:
What is the purpose of M12 cable coding?
M12 cable coding ensures that connectors with different coding types cannot be mistakenly connected, preventing potential damage to equipment and ensuring proper data transmission and power delivery. It plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and reliability of industrial connectivity.
Can I use different coding types of M12 cables interchangeably?
No, different coding types of M12 cables are not interchangeable. Each coding type has a unique keying and pin configuration that is specific to its intended application. Using incompatible coding types can result in incorrect connections and may lead to data transmission errors or equipment damage.
How do I identify the coding type of an M12 cable?
M12 cables are typically color-coded and labeled to indicate their coding type. A-coded cables are commonly black, B-coded cables are white, D-coded cables are green, and X-coded cables are purple. Additionally, the connectors themselves may have corresponding coding symbols or markings.
Can I mix different coding types of M12 cables within the same network?
While it is generally recommended to use the same coding type within a network to ensure compatibility and standardization, certain scenarios may require the use of different coding types. In such cases, it is essential to ensure that the connectors and equipment on both ends of the cable are compatible with the respective coding types.
Are there any industry standards or guidelines for M12 cable coding?
Yes, there are industry standards and guidelines that define the coding types and their specific applications. For example, IEC 61076-2-101 standardizes A and B-coded M12 connectors, while IEC 61076-2-109 standardizes D-coded M12 connectors. These standards ensure interoperability and compatibility within specific industrial sectors.
Can I upgrade my existing M12 cables to a higher coding type?
In some cases, it may be possible to upgrade existing M12 cables to a higher coding type, depending on the compatibility of the connectors and equipment involved. However, it is essential to carefully assess the requirements and limitations of the existing infrastructure to ensure a successful upgrade without causing any disruptions.
Are there any limitations to consider when using M12 cables with higher data rates?
M12 cables with higher data rates, such as X-coded cables for 10 Gigabit Ethernet, have certain limitations. While they offer increased bandwidth, they may have limited power capacity compared to other coding types. Therefore, it is crucial to consider both data transmission requirements and power needs when selecting a coding type for high-speed applications.
Conclusion
Selecting the right M12 cable coding is crucial to ensure reliable and efficient connectivity in industrial applications. By understanding the different coding types, their characteristics, applications, and considering factors like environmental conditions, industry standards, and connectivity needs, you can make an informed decision.
As technology evolves, new coding types may emerge to meet the demands of future industrial connectivity. Stay updated with the latest advancements and ensure compatibility with existing systems when upgrading or expanding your network.